KEY LEGAL COMPLIANCES – CHECKLIST FOR NEWLY-ESTABLISHED COMPANIES (P3)
Part 3: Compliance with labour laws and ensuring workers’ rights and interests
Adherence to the laws and regulations right from the beginning will help all the business activities of the company be operated effectively and avoid legal risks. Regulatory compliance requires companies to aspire and attempt to ensure that they are aware of and take steps to comply with relevant laws, rules, policies, and regulations. Due to the increasing number of laws and especially rules and regulations churned out every year, it is also important for companies to follow up on changes in the legal system.
Our Clients engaging in the retainer services at Le & Associates will always be advised thoroughly and comprehensively on legal issues right from the get-go. Within this article, we will provide you with the basic provisions that new businesses should consider as follows:
- Compliance with laws on investment and laws on enterprises (Link: Part 1)
- Compliance with laws on finance, tax, and accounting regime (Link: Part 2)
- Compliance with laws on employment and protection of employee’s rights and interests (Link: Part 3)
16. Recruitment and signing Employment Contracts
16.1 Recruitment
The labour force plays an important role in production and commercial activities as well as the sustainable development of enterprises. Accordingly, the hiring process is always on the top of the to-do list that your company needs to carefully carry out right after its establishment.
a. Complying with laws during your recruitment process
The enterprise has the right to directly carry out the recruitment process or to choose suitable applicants through services provided by employment service organizations or labour sub-lease enterprises.
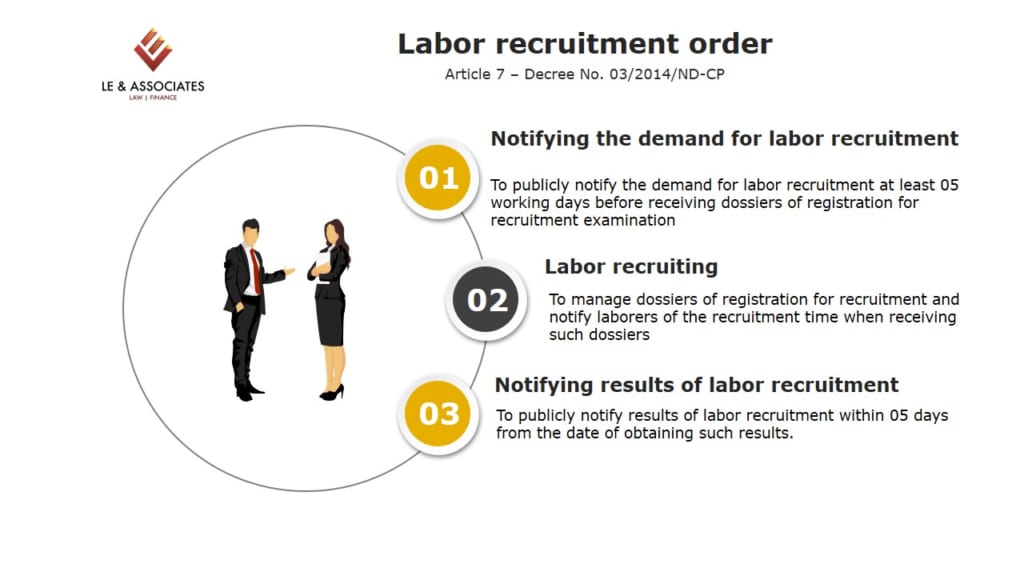
b. Must- follow steps in the recruitment process
The Vietnam laws on Labor stipulates a number of steps employers must take to stay on the right side of the law when it comes to recruiting employees. Those are described as follows:
Note:
- The applicants desiring to be returned their resume and certificates as prescribed in Article 7.5 of Decree No. 03/2014/ND-CP need to submit a written request within 03 months from the date of notifying the recruitment result.
- For applicants who fail or be absent from the recruitment examination, the job hunters shall return all documents received from the applicants within 5 working days after receiving the applicant’s written request.
16.2 Going into Employment Contracts
Before assigning an employee to work, the employer must enter into an employment contract with the employee. The Labor Code 2019 defines: “An employment contract is an agreement between the employee and the employer on the paid job, working conditions, rights and obligations of each party in the employer-employee relationship”. When going into the employment contract must be followed with the following principles:
a. Must-follow principles:
- The Parties voluntarily, equitably, affably, cooperatively and truthfully enter into the employment contract;
- The freedom of contract shall be respected providing that there is not any term violating the laws, the collective labour agreement, and the social ethics.
b. Types of employment contracts
The employment contracts must fall within one of the specified types as follows:
- Indefinite-term employment contract: the employment contract is not concluded for a certain period of the employer-employee relationship;
- Fixed-term employment contracts: the employment contract specifying the term for the employer-employee relationship as well as the expiry date of the contract which shall not exceed 36 months from the effective date of the contract.
- Seasonal or work-specific employment contracts that have a duration of under 12 months.
c. Forms of employment contracts
- Employment contracts must be established in writing and made in 02 copies, one to be kept by the employee and the other by the employer;
- The electronic employment contract signed through electronic means shall be in the form of data messages in accordance with the law on electronic transactions is recognized with legal validity similar to a written ones;
- For temporary jobs with terms under 01 month, the parties may go into verbal employment contract except for the cases as below:
+ The seasonal or specific job that has a duration of under 12 months;
+ The employment contract in which one party is a person under 15 years old;
+ The employment contract in which one party is a domestic worker.
d. Contents must be included in employment contracts
Every employment contract must include the following terms:
- Name, address of the employer and the full name, title of the employer representative;
- The full name, date of birth, gender, residence, ID number/Citizen ID number/Passport of the employee;
- Employee’s job duties and working location;
- The employment contract term;
- The salary, method of payment, salary payment term, allowances, and other additional benefits;
- The promotion policy, salary review schedule;
- The working hours, break & rest time;
- The labour protection equipment/ tools for employees;
- Social insurance & medical insurance and unemployment insurance;
- Vocational training and improvement courses.
17. Reports on the workforce
Within 30 days as from starting running the business, the employer has to declare the employment to the Labor, War Invalids and Social Affairs Division or the Department of Labor, War Invalids and Social Affairs (if the enterprise is located in an industrial park) of the city/province where its head office, branch or representative office is located. The number of staff which is listed on the report does not include those on probation.
The notice must be attached with the following documents:
- The copy of the enterprise registration certificate;
- The employer declaration sheet (Form no. 05 issued together with Circular No. 23/2014/TT-BLDTBXH).
Note: Enterprises must still report on labour utilization if after 30 days there is no labour working at the enterprise.
18. Notification of the number of employees working at newly-established enterprises
Within 30 days from the date of establishment, enterprises are responsible for sending a notice of the number of employees working at the enterprises. (Form No. 28 issued together with Circular No. 28/2015/TT-BLDTBXH) to the Employment Service Center where the enterprise is headquartered.
19. Building salary scale/ grade, payroll and labour productivity norm
The enterprise is obliged to build the salary scale, payroll, and labour productivity norm as the cornerstones for labour recruitment and employment, salary negotiation in the employment contracts, and make employee compensations.
Enterprises must base on the current local minimum salary to stipulate the salary for each job level, position, typical groups of job in accordance with the principles prescribed by law.
The enterprise is obliged to consult with the representative organization of the labour collective at the grassroots level (for enterprises have the representative organization of employees at the grassroots level) when building its salary scale/ grade, payroll, and labour productivity norms.
The salary scale/ grade, payroll, and labour productivity norms must be publicly announced at the workplace before official implementation.
20. Building the internal labor regulations
Enterprises must issue their internal labour regulations. For enterprises having more than 09 employees, the internal labour regulation must be in written form.
Within 10 days from the date of promulgation of labour rule, the enterprise must submit a dossier for registration of its internal labour regulations at the provincial labour-management authority where the enterprise registers its business.
In case an enterprise has branches, production, and business establishments located in different cities/ provinces, it must send the registered internal labour regulations to the labour specialized authorities of the provincial People’s Committees where its branches, units, and facilities are located.
21. Establishment of Trade Union Organization
Enterprises with at least 05 trade unionists and over or employees handing in the volunteer application form to join the Vietnam Trade Union, and are eligible to establish Trade Union organizations according to the provisions of the Trade Union Law and the Vietnam Trade Union Statute must, at least 06 months from the day the enterprise is established and come into practice, form a trade union organization in accordance with the law.
After the aforementioned period, if the enterprise is yet to form the trade union organization, the superior trade union authority has the right to establish an Interim executive board of the Trade Union of the enterprise.
***
The aforementioned issues for newly-established enterprises provided in this article are aimed to help you have useful information to actively perform necessary works for your businesses in accordance with the laws.
Please contact us if you have any legal issues via our hotline, email, or our office address.